Cloud Data Encryption is the process of converting data from plain text to an unreadable format, like ciphertext, before transferring it to and storing it in the cloud.
Cloud Data Encryption, like any other type of data encryption, renders the information unintelligible and thus useless in the absence of the encryption keys. This holds true even if the data is misplaced, stolen, or decided to share with an unauthorized user.
Encryption is widely regarded as one of the most active ingredients of a company’s cybersecurity strategy. Cloud encryption addresses other critical security issues in addition to securing information from misuse. These include:
- Observance of regulatory standards governing data security and confidentiality
- Improved security against unapproved data access by other public cloud tenants
- In some cases, releasing the organization from the obligation to disclose breaches or even other security events.
Contents
What Is the Process of Cloud Encryption?
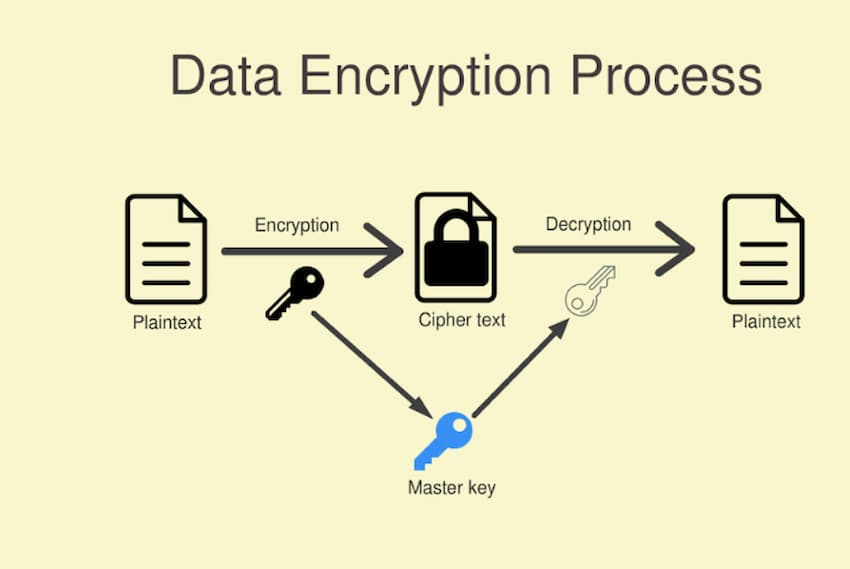
Encryption encodes data using advanced algorithms, rendering it pointless to any user without an encryption key. Authorized users use the key to decipher the data, converting the hidden information into a usable form. Keys are only generated and distributed to trusted parties whose identities have been established and verified using some type of multi-factor authentication.
Cloud Data Encryption is intended to protect data as it travels to and from cloud-based apps and when it is saved on the cloud network. This is referred to as data in transit as well as data at rest.
Data encryption in transit
The HTTPS protocol, which helps to add a security sockets layer to the standard IP protocol, automatically encrypts a substantial portion of data in transit. SSL encrypts all activity, making sure that only authorized individuals have access to session information. As a result, if unauthorized access intercepts data sent during the session, the content is meaningless. A digital key is used to complete decoding at the user level.
At-rest data encryption
Data encryption for stored information on the cloud network ensures that if the data is lost, stolen, or inadvertently shared, the contents are rendered virtually useless in the absence of the encryption key. Keys, once again, are only made accessible to authorized users. The software application manages decryption/encryption for data at rest, just as it does for data in transit.
Algorithms for Encryption
For cloud-based data, there are 2 basic encryption algorithms:
The decryption and encryption keys are identical when using symmetric encryption. This technique is usually used to encrypt large amounts of data. While it is generally simpler and faster to implement than the asymmetric option, it is less safe in that anybody who has access to the encryption key can understand the data.
Asymmetric encryption: Encodes or decodes data using two keys—a private key and a public authentication token. The keys are linked, yet they’re not the same. This method increases security by requiring users to have both a public, freely distributable key and just a personal token in order to access the data.
The Advantages of Cloud Data Encryption

Encryption is one of the most important safeguards that businesses can use to protect their data, other sensitive information, and intellectual property (IP), along with the data of their customers. It also addresses privacy and security standards and regulations.
The following are some of the advantages of cloud encryption:
- Security: End-to-end encryption protects sensitive information, such as customer data, when it’s in transit or at rest across one of these devices or between users.
- Compliance: Regulations and standards governing data privacy and protection, such as the Federal Information Processing Standards and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, require organizations to encrypt all sensitive customer data. While malicious actors can alter or manipulate encrypted data, such activity is relatively simple to identify by authorized users.
- Risk reduction: Organizations may be excluded from disclosing a data breach in certain circumstances if the data was encrypted, which markedly minimizes the likelihood of both reputational harm but also lawsuits or other legal action linked with a security event.
Is it necessary to encrypt my cloud storage?
Cloud Data Encryption constitutes one of the most specific measures that businesses can take to safeguard their data and sensitive customer information. Organizations should work with their cybersecurity partner to choose the best third-party encryption tool as well as integrate it into their existing security technology stack.
The following are some topics to consult with your cybersecurity partner about cloud storage encryption:
- How to recognize information that calls for encryption, either because it is sensitive or to comply with regulatory standards.
- The date and location where data will be encrypted, as well as the procedure that will be used
- How to supplement the existing cloud security measures of the cloud provider or CSP
- How will access keys be generated and distributed in order to mitigate the danger associated with weak passwords?
- Who will be in charge of key management and storage?
- In the event of a breach with the CSP, how and where will encrypted data be backed up?
- How a cloud access security broker can improve visibility and coordinate data access across the organization